Coupled land-water-climate-human dynamics in the Amazon Basin

This NSF-funded project (2018-2022, PI Dr. Katrina Mullan, U Montana) quantified feedbacks among land use, climate, water, and human well-being and behavior in the Brazilian Amazon. The project will couple models of climate (Dr. Fernando de Sales, SDSU) with land surface models, hydrological data and models (Biggs), socioeconomic surveys, and agent-based models of human decisions to quantitatively link the hydroclimate, humans, and land cover outcomes. See SDSU media coverage here and on page 10 here. See the project website here, and project resources here. Brazil-wide Water Resources Network ProfAgua aqui.
Plastic and anthropogenic debris mapping and modeling
Plastic and other anthropogenic debris are a threat to marine and freshwater ecosystems, and present hazards by blocking drainage and increasing flood hazard. We have projects in the US and Mexico designed to help map, monitor, and model the mass balance of anthropogenic debris.
Figure credit: Elena Aguilar
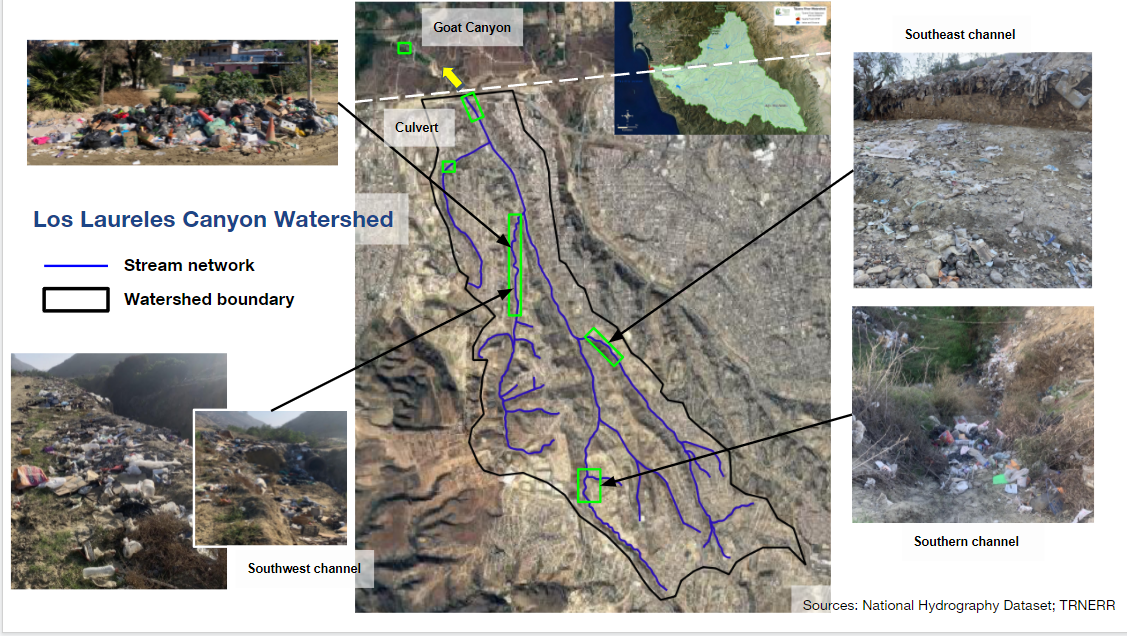
Land cover, runoff and erosion in Tijuana, Mexico
 This series of projects, funded by the US EPA, aimed to map and model land cover, runoff and erosion from urbanized watersheds in Mexico that drain to the ecologically-valuable Tijuana Estuary. Projects included measurement and modeling of runoff and sediment load, mapping of gully and channel erosion, and mapping land cover and socioeconomic status. Students involved: Garrett McGurk, Ben Downing, Kris Taniguchi (PhD 2018), Napoleon Gudino-Elizondo (PhD 2018).
This series of projects, funded by the US EPA, aimed to map and model land cover, runoff and erosion from urbanized watersheds in Mexico that drain to the ecologically-valuable Tijuana Estuary. Projects included measurement and modeling of runoff and sediment load, mapping of gully and channel erosion, and mapping land cover and socioeconomic status. Students involved: Garrett McGurk, Ben Downing, Kris Taniguchi (PhD 2018), Napoleon Gudino-Elizondo (PhD 2018).
Land Use Change, Crop water use and Water Resources
 Water scarcity both drives and is impacted by land cover change. This series of projects aims to map crop water use and land cover change in irrigated agricultural regions, including applications in India, Southern Africa, California and on the US-Mexico border, and to document the major drivers of those changes through mixed methods approaches that integrate remote sensing for automated mapping of crop water use (evapotranspiration) and land cover, quantitative survey data, and qualitative interviews. Applications in California and on the US-Mexico border are supported in part through the NOAA CREST program. Students involved: Yelena Granovskaya, Joel Kramer, Gabriela Morales, Alex Messina, Nadine Barham, Gabriela Morales.
Water scarcity both drives and is impacted by land cover change. This series of projects aims to map crop water use and land cover change in irrigated agricultural regions, including applications in India, Southern Africa, California and on the US-Mexico border, and to document the major drivers of those changes through mixed methods approaches that integrate remote sensing for automated mapping of crop water use (evapotranspiration) and land cover, quantitative survey data, and qualitative interviews. Applications in California and on the US-Mexico border are supported in part through the NOAA CREST program. Students involved: Yelena Granovskaya, Joel Kramer, Gabriela Morales, Alex Messina, Nadine Barham, Gabriela Morales.
Biggs, T. W., Marshall, M., & *Messina, A. (2016). Mapping daily and seasonal evapotranspiration from irrigated crops using global climate grids and satellite imagery: Automation and methods comparison. Water Resources Research, 52(9), 7311–7326. http://doi.org/10.1002/2016WR019107
Hess, T. M., Sumberg, J., Biggs, T., Georgescu, M., Haro-Monteagudo, D., Jewitt, G., … Knox, J. W. (2016). A sweet deal? Sugarcane, water and agricultural transformation in Sub-Saharan Africa. Global Environmental Change, 39, 181–194. http://doi.org/http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2016.05.003
Biggs, T. W., Gangadhara Rao, P., & Bharati, L. (2010). Mapping agricultural responses to water supply shocks in large irrigation systems, southern India. Agricultural Water Management, 97(6), 924–932. Retrieved from http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/B6T3X-4YJCTMK-1/2/94fb2a6a5321f73c294d33692cc1ec4c
Land-Based Pollution of Coral Reefs, American Samoa
Sediment and nutrient loading impacts the health of coral reefs. This series of projects funded by NOAA and NFWF quantified the sources of sediment in a watershed draining to a sediment-impacted reef, and documented the impact of mitigation activities on sediment load. Students involved: Alex Messina (PhD, 2016), Greg McCormick (MS 2016), Sean Quezada (MS)
Stable isotopes for detection of runoff sources and evaporation
Stable isotopes of water (18O and D) can be used for both source identification and quantification of evaporation rates. We have used isotopes to estimate evaporation fractions in high elevation-lakes in the Himalaya (funded by WWF-India), and are currently using them to separate dry weather flows in San Diego into local and imported (Sierra Nevada, Colorado River) sources, funded by the County of San Diego.
Biggs, T. W., Lai, C.-T., Chandan, P., *Lee, R. M., *Messina, A., Lesher, R. S., & Khatoon, N. (2015). Evaporative fractions and elevation effects on stable isotopes of high elevation lakes and streams in arid western Himalaya. Journal of Hydrology, 522(0), 239–249. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.12.023
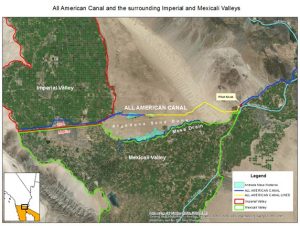
Groundwater change and water quality in the Mexicali Valley
 These projects mapped changes in groundwater levels and water quality and how they have changed in the Imperial and Mexicali Valleys from 1980-2018, a period when land use and water management changed dramatically. The results of this project will help identify areas that are sensitive to future land use change, and where water quality impairs agricultural production. Students involved: Rodney Feddema (MS), Sarah Roberts (MS).
These projects mapped changes in groundwater levels and water quality and how they have changed in the Imperial and Mexicali Valleys from 1980-2018, a period when land use and water management changed dramatically. The results of this project will help identify areas that are sensitive to future land use change, and where water quality impairs agricultural production. Students involved: Rodney Feddema (MS), Sarah Roberts (MS).
Land cover and socioeconomic status, 2008-2010
Funded by Southwest Consortium on Environmental Research and Policy (SCERP), US EPA,
This project aimed to map land cover and its relationship to socioeconomic status in Tijuana.
Biggs, T. W., *Anderson, W. G., & Pombo, O. A. 2014. Concrete and Poverty, Vegetation and Wealth? A Counterexample from Remote Sensing of Socioeconomic Indicators on the U.S.–Mexico Border. The Professional Geographer, 1–14. http://doi.org/10.1080/00330124.2014.905161
Biggs, T. W., *Atkinson, E., Powell, R., & Ojeda-Revah, L. (2010). Land cover following rapid urbanization on the US–Mexico border: Implications for conceptual models of urban watershed processes. Landscape and Urban Planning, 96(2), 78–87. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2010.02.005
Anoxia and hydrodynamics in lakes and reservoirs
Land use change can change loading rates of nutrients to water bodies, sometimes resulting in seasonal anoxia in lakes and reservoirs. Aeration devices can be used to oxygenate anoxic waters. In one cooperative project between SDSU and the San Diego River Park Foundation, members of the Biggs Lab are monitoring the impact of aerators on dissolved oxygen in pools of the lower San Diego River. See here a summary of SDSU projects on the lower San Diego River. Previous projects analyzed and modelled dissolved oxygen in reservoirs of San Diego County. Students involved: Rodney Feddema (MS), Tigran Ghanuskovyan (MPH), Environmental Science Undergraduates, Kimberly Livers (BS), Raymond Lee.
*Lee, R., Biggs, T., & Fang, X. (2018). Thermal and Hydrodynamic Changes under a Warmer Climate in a Variably Stratified Hypereutrophic Reservoir. Water . https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091284
*Lee, R. M., & Biggs, T. W. (2015). Impacts of land use, climate variability, and management on thermal structure, anoxia, and transparency in hypereutrophic urban water supply reservoirs. Hydrobiologia, 745(1). http://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-014-2112-1
* indicates a student co-author.